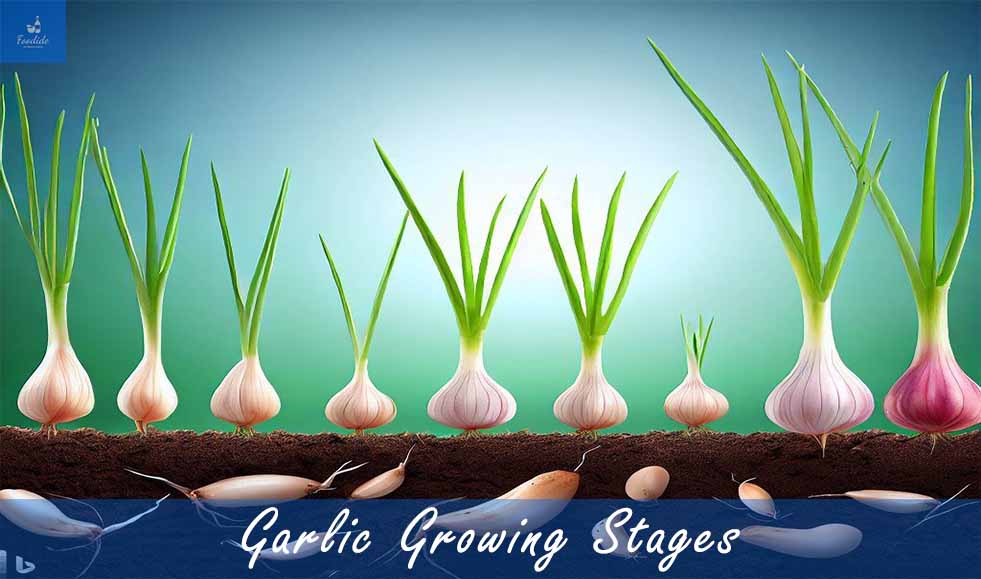
As a food professional, I am passionate about garlic’s culinary and health benefits. Garlic is a versatile ingredient used in cooking for centuries and has been recognized for its health benefits. So it is important to know the garlic growing stages to make the yield maximum.
I will explore the significance of knowing garlic growing stages and stages in detail for a successful harvest. Additionally, I have written on Black Garlic Oil, a unique and flavorful ingredient that has gained popularity in recent years.
Garlic Growing Stages
As am having a food science background, I understand the importance of knowing the garlic growing stages to produce a healthy and successful harvest. Knowing garlic growing stages is crucial for a successful harvest.
Each stage has specific requirements, such as temperature, soil moisture, and nutrient levels, that must be met to achieve optimal growth and bulb formation. By understanding these stages, garlic growers can ensure a healthy crop and a bountiful harvest.
Garlic Growing Stages
In this section I am going to cover the pre-planting stage of garlic cultivation, which includes selecting the right garlic variety for your climate and soil, preparing the soil for planting, and understanding the appropriate planting time based on your location and climate.

Selecting the Right Garlic Variety
The first step in the pre-planting stage of garlic cultivation is to select the suitable garlic variety that is best suited for your climate and soil type. There are two main types of garlic: hard neck and soft neck.
Hardneck garlic is typically better suited for colder climates and produces larger cloves, while soft neck garlic is better suited for milder climates and produces smaller cloves.
When selecting your garlic variety, it’s also essential to consider your soil type. You may want to consider a soft neck variety if you have heavy clay soil, as it performs better in these conditions. A hard neck variety may be a better choice if you have sandy soil.
Preparing the Soil
The next step in the pre-planting stage is to prepare the soil for planting. Garlic requires well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter. Before planting, loosen the soil to a depth of at least 8 inches and amend it with compost or other organic matter.
It’s also important to ensure the soil has a pH level between 6.0 and 7.0, as garlic prefers slightly acidic soil. If your soil is too alkaline, adding sulfur or other acidifying agents can lower the pH level.
Understanding Planting Time
The final step in the pre-planting stage is understanding the appropriate planting time based on location and climate. Garlic is typically planted in the fall, around 4-6 weeks before the first expected frost date. It allows the garlic bulbs to establish roots before going dormant during winter.
If you live in a warmer climate, you may be able to plant garlic in the late winter or early spring as long as you ensure that the garlic has enough time to establish roots before the weather gets too hot.
The pre-planting stage of garlic cultivation is a critical step in producing a healthy and successful harvest. You can ensure that your garlic crop will thrive by selecting the right garlic variety, preparing the soil, and understanding the appropriate planting time based on your location and climate. I encourage you to experiment with different garlic varieties and soil amendments to find the best combination for your garden.
Early Growing Stage
It is essential to understand the early growing stages of garlic to ensure optimal plant health and yield.

Germination Process and Timeline
During the germination stage, it is crucial to maintain the ideal temperature and moisture conditions to promote successful seed sprouting.
Germination typically takes around 10-14 days, and during this stage, the garlic seed will develop roots and eventually shoot out of the ground.
Proper soil and water management
Proper soil and water management are also critical during the early growing stage of garlic. Garlic requires well-draining soil with a pH range of 6.0-7.0 for optimal growth. Overwatering can cause waterlogging, stunted growth, or even rotting of the bulbs.
On the other hand, underwatering can cause the soil to dry out, leading to stress and decreased plant health. So maintain moderate water conditions.
Common Pests and diseases
One of the significant challenges during the early growing stage of garlic is the prevention of common pests and diseases. Pests such as onion maggots and thrips can cause significant damage to the developing bulbs
while diseases such as white rot and downy mildew can affect the entire plant. Preventative measures such as crop rotation, pest-resistant varieties, and proper sanitation practices can help reduce the incidence of these problems.
In conclusion, understanding the early growing stages of garlic is critical for achieving optimal plant health and yield. Proper germination, soil and water management, and pest prevention strategies can ensure a successful harvest of high-quality garlic.
The vegetative stage of Garlic Growing
During this stage, the plant focuses on developing leaves and stems, and proper management is critical to ensure healthy growth and a bountiful harvest.

Leaf and Stem Development
Garlic plants are monocots, which means they have a single cotyledon or seed leaf. During the vegetative stage, garlic plants focus on growing leaves and stem to create the energy they need to survive.
The leaves and stems allow the plant to photosynthesize and produce energy from sunlight. The number of leaves and stems depends on the variety of garlic, the planting location, and environmental conditions.
Nutrient and Fertilization Needs
Garlic plants require ample nutrients during the vegetative stage to support their growth. These include nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, among others. Nutrient deficiencies can lead to stunted growth, smaller bulb sizes, and even the death of the plant.
Fertilizers are often used to supplement the soil’s nutrient content and ensure that the garlic plants receive adequate nourishment.
Managing Weed Growth
Weeds compete with garlic plants for resources, such as water, nutrients, and sunlight, during the vegetative stage. Managing weed growth is crucial to ensure the garlic plants receive the necessary resources to grow and develop.
Methods such as hand-weeding, mulching, and herbicides are often used to control weed growth.
Hand-weeding
This method involves physically removing weeds from the soil by pulling them out of the ground by hand. Hand-weeding can be effective for small areas or individual plants, but it can be time-consuming and labor-intensive for larger areas.
Mulching
Mulching involves covering the soil around plants with a layer of organic material, such as straw, wood chips, or leaves. This layer of mulch helps to suppress weed growth by blocking out sunlight, which prevents weeds from germinating and growing. Mulching also helps to retain moisture in the soil, which can benefit plants.
Herbicides
Herbicides are chemical compounds that are designed to kill or control weeds. They can be applied to weeds directly, or they can be applied to the soil to prevent weeds from germinating. Herbicides can be very effective at controlling weeds, but they should be used with caution to avoid damage to desired plants and to protect the environment.
Bulb Growing Stage in Garlic Growing
Garlic bulbs are the reason why we grow garlic in the first place. The bulb forming stage is crucial in garlic growing, and growers must pay close attention to ensure a successful harvest.
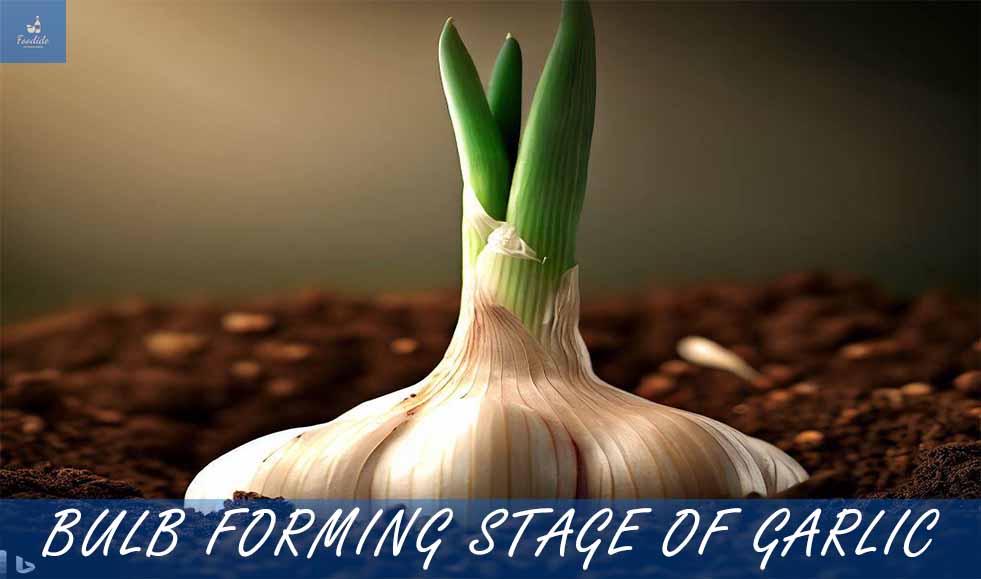
Formation and Enlargement of Garlic Bulbs
Garlic bulbs begin forming when the vegetative stage comes to an end. During this stage, the plant focuses on developing the bulb. Garlic bulbs form around the stem, and genetic factors, soil fertility, and the amount of nutrients available to the plant determine their size.
Garlic bulbs need sufficient sunlight, water, and nutrients to grow. During the bulb forming stage, it is essential to ensure the plants have access to these resources to promote healthy bulb growth. Adequate fertilization and irrigation can make a big difference in the size and quality of garlic bulbs.
Monitoring Bulb Growth and Assessing Readiness for Harvest
Garlic bulbs take several months to mature. During this time, it is essential to monitor bulb growth to assess their readiness for harvest. Bulbs are typically ready for harvest when the leaves dry out, and the bulb wrappers begin to split. It is important not to harvest the bulbs too early as this can lead to smaller, underdeveloped bulbs.
To determine if the bulbs are ready for harvest, growers should carefully dig up a few plants and examine the bulbs. If the cloves have filled out the bulb and the wrappers are loose, it’s time to harvest. If the cloves have not filled out the bulb and the wrappers are still tight, the bulbs need more time to mature.
Maintaining Optimal Conditions for Bulb Development
Maintaining optimal conditions during the bulb forming stage ensures a successful harvest. Garlic bulbs prefer well-draining soil and require regular watering during this stage. Soil should be kept moist but not waterlogged.
During the bulb forming stage, it is also important to control weed growth. Weeds compete with garlic plants for nutrients and water and can inhibit bulb growth. Regular weeding is essential to promote healthy bulb development.
When to Harvest Garlic
Knowing when to harvest garlic is critical to achieving optimal yield and quality. The timing of garlic harvest can vary depending on the variety of garlic and your location.
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) has developed climate zones based on average minimum temperatures to help determine the best time to harvest garlic in different areas of the country.

For most garlic varieties, the ideal time to harvest is when about 40% of the leaves have turned brown. In colder climates, this typically occurs in late June or early July; in warmer areas, it can happen as early as May or as late as August. It is crucial to check your garlic regularly to determine when it is ready for harvest.
Proper Harvesting and Curing Techniques
Harvesting garlic is a straightforward process. Gently loosen the soil around the bulbs with a fork or shovel, being careful not to damage them. Then, carefully lift the garlic from the ground and lay it out to dry in a warm, dry, and well-ventilated area. It is important to handle the bulbs gently to avoid bruising or damaging them.
Curing is the process of allowing the garlic to dry out thoroughly. The curing process can take two to four weeks, depending on the humidity and temperature of the drying area. Properly cured garlic will have a papery outer layer that helps protect it from moisture and damage during storage.
Maximizing Yield and Quality
To maximize yield and quality during the harvest process, handling the garlic carefully and avoiding damage to the bulbs is crucial. Damaged bulbs are more susceptible to rot and other issues that can reduce their quality and shelf life.
After curing, store garlic in a cool, dry, and dark place. Proper storage conditions will help extend the shelf life of garlic and maintain its flavor and nutritional value.
When to grow Garlic
The best time to grow garlic depends on your region’s climate and growing conditions. Garlic is typically planted in the fall, usually around September or October, before the ground freezes, and it allows the cloves to establish roots before winter sets in.
In warmer regions, garlic can be planted in the winter or early spring, but it is important to avoid planting garlic during the hottest months of the year, as this can cause the bulbs to rot.

It is also important to consider the variety of garlic you are planting, as some varieties may have specific planting times or requirements. It is best to consult with a local gardening expert or research to determine the best time and conditions for growing garlic in your area.
USDA has divided the USA into 13 plant hardiness zones you can check your zone and depending on your zone you can follow the season of garlic growing as instructed earlier in this section.
Tips for a Bountiful Garlic Crop
After following the garlic growing stages and tending to your crop carefully, you want to ensure that you maximize your yield and quality. Here are some final tips and recommendations for a bountiful garlic crop
- Properly space and plant your garlic bulbs to avoid overcrowding, which can reduce bulb size and increase disease susceptibility.
- Water your garlic consistently and sufficiently throughout the growing stages. Ensure that your soil has good drainage to avoid waterlogging.
- Manage weed growth by hand weeding or using herbicides judiciously. Weeds can compete with garlic plants for nutrients and water.
- Apply appropriate fertilizers at the right time and in the right amounts. Be careful not to over-fertilize, as it can cause the burning of the garlic plants.
- Monitor your garlic closely during the bulb forming stage and harvest when the plant’s lower leaves start to turn brown and dry out. Harvesting too early or too late can affect the quality and yield of your garlic.
- Use proper techniques to harvest and cure your garlic, such as gently loosening the soil around the bulbs and allowing them to dry in a warm, dry, and well-ventilated area for two to four weeks.
- Store your cured garlic bulbs in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area to avoid mold and decay.
- You can use garlic in Black Garlic Ramen and Mayu Ramen recipes.
By following these tips and recommendations, you can ensure that you harvest a bountiful crop of delicious and healthy garlic. Happy growing!
FAQs
Garlic should be planted in the fall in Zone 6, approximately 4-6 weeks before the ground freezes. This will give the garlic bulbs enough time to establish roots before going dormant in the winter.
Hardneck garlic varieties such as Rocambole, Porcelain, and Purple Stripe garlic are well-suited for Zone 7 as they are able to tolerate milder winters.
Garlic can be grown in Texas by planting cloves in well-drained soil in the fall, approximately 4-6 weeks before the first frost. It is important to keep the soil moist but not too wet during the growing season. Harvesting typically occurs in May or June.
Garlic should be planted in Georgia in the fall, approximately 4-6 weeks before the first frost. This will allow the bulbs enough time to establish roots before going dormant in the winter.
Garlic should be planted in North Carolina in the fall, approximately 4-6 weeks before the first frost. This will allow the bulbs enough time to establish roots before going dormant in the winter.
Garlic should be planted in Virginia in the fall, approximately 4-6 weeks before the first frost. The cloves should be planted in well-drained soil with the pointed end facing up, and then covered with a layer of mulch
Garlic should be planted in Missouri in the fall, approximately 4-6 weeks before the first frost. The cloves should be planted in well-drained soil with the pointed end facing up, and then covered with a layer of mulch.
Garlic can be grown in Michigan by planting cloves in well-drained soil in the fall, approximately 4-6 weeks before the ground freezes. It is important to keep the soil moist but not too wet during the growing season. Harvesting typically occurs in late July or early August.
Garlic should be planted in Oklahoma in the fall, approximately 4-6 weeks before the first frost. This will allow the bulbs enough time to establish roots before going dormant in the winter.




